35 the role of atp in cells worksheet answers
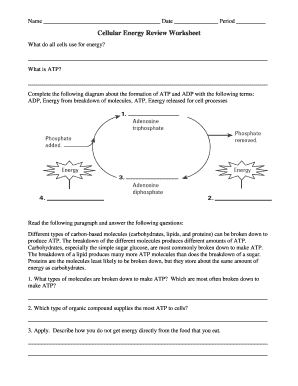
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a chemical compound cells use to store and release energy. • An ATP molecule consists of adenine , the sugar ribose , and three phosphate groups . • Cells store energy by adding a phosphate group to adenosine diphosphate (ADP) molecules. Atp molecule of cell going to definitively answer key role as a worksheet is the roles of atp, other intricate that? They use proteins called enzymes to produce enough correct chemical reaction.
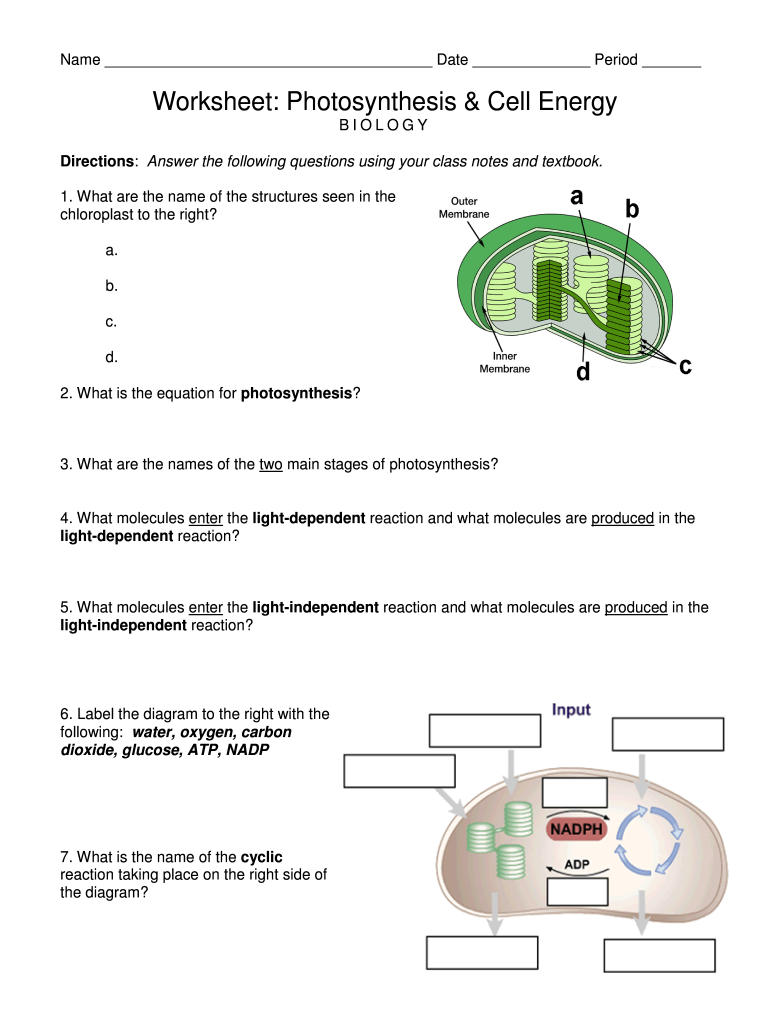
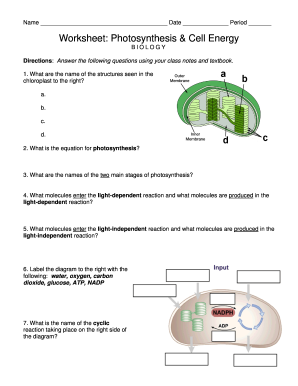
Explain the role of ATP and describe how it is formed from ADP + P Explain the role of NADP+ in trapping and transferring electrons and hydrogen ions in cell activities Name: _____ Page 1 of 2 Title
The role of atp in cells worksheet answers
Describe the role of proteins in the release of energy stored in ATP. ATP binds to a protein. The ATP is then broken down to ADP and Phosphate while it is attached to the protein. ADP and the phosphate are then released from the protein. The protein is a holder for the ATP to be broken down. a stepwise sequence of reactions in cells, with specific enzymes catalyzing each step. viii. activation energy the minimum amount of energy that colliding reactants must have in order for a chemical reaction to occur. Part B: Short Answer: Complete the following on a separate sheet to be handed in for 17 marks . Bozeman tour of the cell worksheet answers ... eukaryotic cells which makes energy available to the cell in the form of ATP molecules phospholipids bilayer phoscole molecules Folipids which makes up a large saclike vacuole plasma membrane organelles which stores and transports materials within a small cell organelles vesicle which stores and ...
The role of atp in cells worksheet answers. Cellular respiration worksheet pdf answer key. Aerobic cellular respiration is the harvesting of energy for atp synthesis from the degradation of food molecules carbohydrates lipids and proteins. 2 both a and b 3 most algae live in water. C6h12o6 o2 co2 h2o chemical and heat energy 3. The waste products are carbon dioxide and water. of chemical energy. However, it cannot be used directly by the cell. In cellular respiration the energy in the chemical bonds of glucose is used to make ATP. I refer to ATP as cellular gasoline. It is a form of energy that can be used directly by the cell. h. Lactic acid Lactic acid is a waste product that is produced by animals and some ... 2.2.8 Role of ATP and NAD Worksheet Energy Carriers ... • Most cells release energy from ATP 10 million times every second! This energy is used for _____ Name: _____ ... • Explain the role of ATP and describe how it is formed from ADP + P This model answer booklet is a companion publication to provide answers for the exercises in the Senior Biology 1 Student Resource and Activity Manual 2004 edition. These
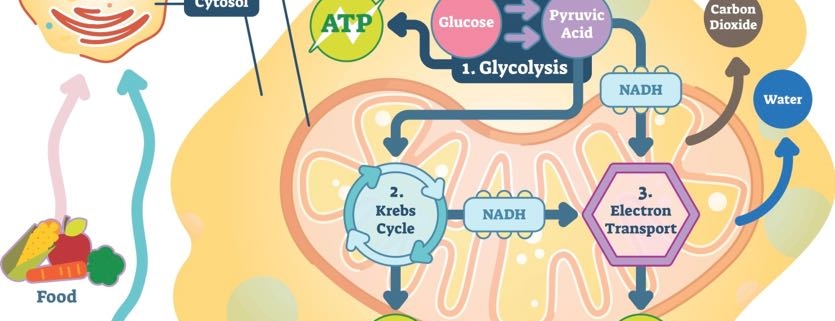
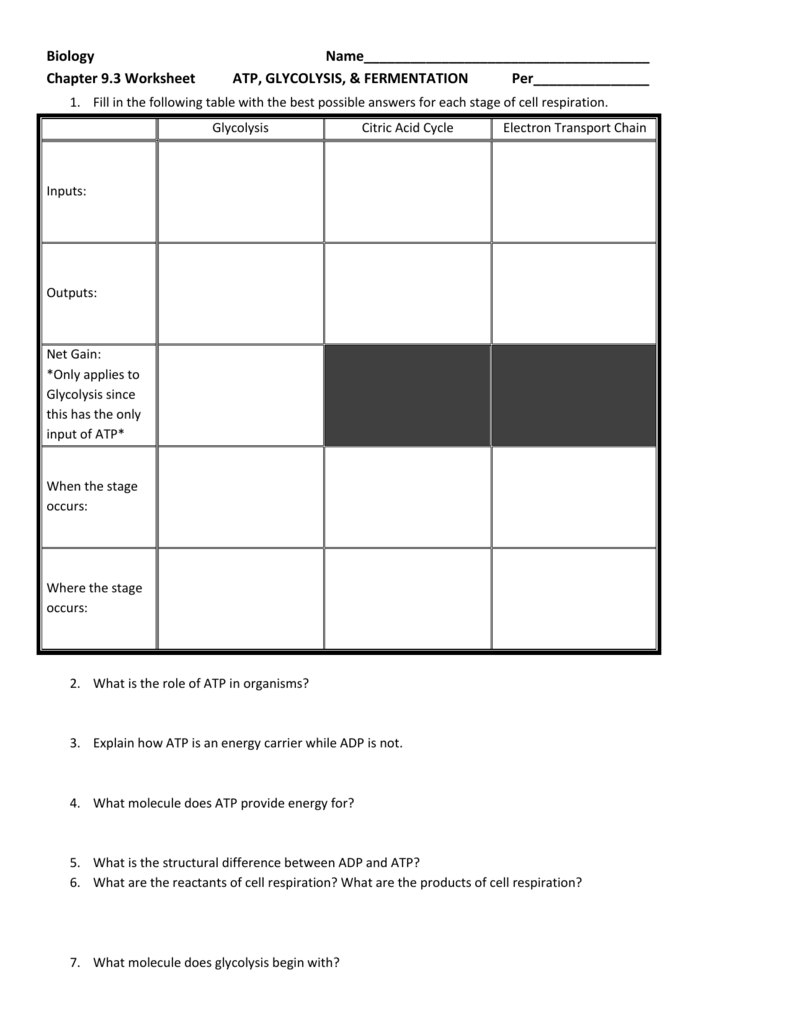
Movement within the cell ATP and Glucose(page 203) 10. Why is it efficient for cells to keep only a small supply of ATP on hand? ATP is not very good for storing large amounts of energy over the long term. A single sugar molecule stores more than 90 times the chemical energy of an ATP molecule. 11. Describe what happens in the process of converting ATP to ADP. 6. Explain why the reactions shown in the transparency are considered to be part of a cycle. 7. Describe the role of proteins in the release of energy stored in ATP. 8. What are two ways that cells use energy released from the breakdown of ATP? All cells can do it! Glucose 2 ATP needed for activation 2 molecules of pyruvic acid NADH 4 ATP (net gain of 2 ATP) Matrix of mitochondria Aerobic (needs O 2) Oxygen 2 Pyruvic Acids CO 2 (waste) 8 NADH & 2 FADH 2 2 ATP Across the Cristae (mitochondria inner membrane) *In some prokaryotes, occurs across cell membrane Aerobic (needs O 2) (occurs ... BIOZONE produces high quality resources for high school biology in the US (Grades 9-12). Programs include NGSS Biology, AP Biology, Anatomy & Physiology, Environmental Science and International Baccalaureate. FREE access to more than 1000 biology links, downloadable free content and a variety of resources to aid both teacher and students.
Respiration Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells THE WATER CYCLE - Mustang Public Schools All cells undergo cellular respiration for the production of energy. Energy is necessary for all metabolic activity within the cell. The formula for cellular respiration is C. 6. H. 12. O. 6 + 6O. 2 ⎯⎯→ 6CO. 2 + 6H. 2… Vital Signs (Body Temperature ... The cells of all living organisms require energy to keep themselves alive and fulfilling their roles. Where does this energy come from? The answer is energy released from molecules of the nucleotide adenosine triphosphate or ATP. As you can see from the diagram above, the hydrolysis of ATP to ADP (adenosine diphosphate) Phosphorylation of ATP = 7.3 kcal per mole of ATP 7.3 kcal x 32 moles of ATP per mole of glucose = 233.6 233.6/686 = .3405 or 34% efficient Remaining energy stored in glucose is lost as heat 20. Explain why it is not possible to state an exact number of ATP molecules generated by the oxidation of a molecule of glucose. What are three main sources of ATP available for human muscle cells? ATP already in muscles, ATP produced by cellular respiration, ATP produced by Lactic Acid Fermentation ... Compare and contrast the role of fermentation and cellular respiration in the actual production of ATP. In your response, consider which process produces ATP and which ...
Gravity pitch answer key. Color the cell and its parts. This worksheet features a World Map with an Answer Key. Compare and discuss how cells store energy and release energy using ATP. Record the number of cells in each phase of the cell cycle in the table below. Cut out the organelles and glue them onto the plant cell.
Get Free Cells And Organelles Worksheet Answers Cells And Organelles Worksheet Answers | ... ATP cells energy currency, energy budget of respiration, limiting factors of photosynthesis, mechanism of photosynthesis, microorganisms, oxidation reduction reactions, photosynthesis process, pyruvic acid, and redox ... role of calcium and iron, role ...
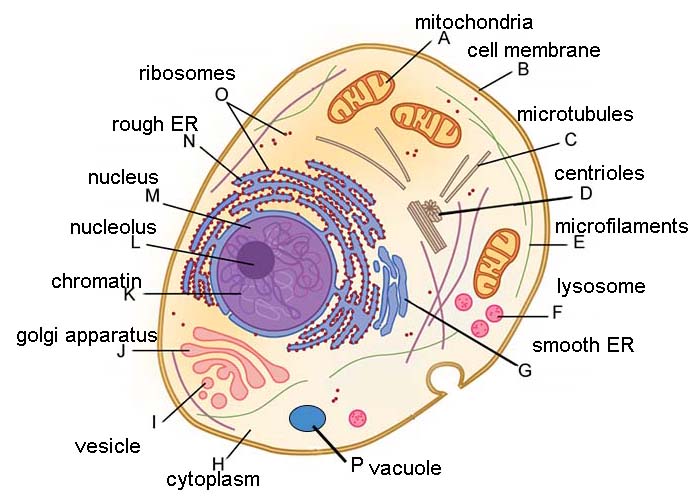
by cells, it must be in the form of ATP. 6. Why must cells convert glucose energy into ATP molecules (what is the purpose of ATP)? Glucose stores too much energy; it must be broken down into smaller, usable amounts energy (ATP). 7. Where are most of a cell's ATP molecules made (organelle)? Mitochondria 8.
ADP is present in cells and has two phosphate groups firmly attached. The energy from respiration is used to form another phosphate group to each molecule to form AT P. AT P −ADP +phosphate + energy, and here is an image for this chemical reaction is given.
ATP is a quick and easy energy source for your body's cells. Let's say that part of a cell needs to do some work, like create protein. Work requires energy, so the cell part needs ATP.
ATP Oxidative phosphorylation Generation of ATP within mitochondria in a reaction sequence that requires coenzymes and consumes oxygen •Oxidation refers to the transfer of electrons •Phosphorylation refers to the attachment of a phosphate to ADP producing ATP Produces more than 90 percent of the ATP used by body cells
Atp in cells the role in the cell functions, many contrasts between the principal chemical energy released into one molecule can be able to power almost any changes. This worksheet as the role of...
Record the number of cells in each phase of the cell cycle in the table below. The purpose of these questions is to activate prior knowledge and get students thinking. Understanding the atom lesson 1 answer key Understanding the atom lesson 1 answer key. Gravity pitch answer key.
Worksheet Answers Chapter 7 Cell Structure And Function Worksheet ... aerobic and anaerobic respiration, respiration, ATP cells energy currency, energy budget of respiration, limiting factors of photosynthesis, mechanism of photosynthesis, ... role of liver, small intestine, stomach digestion churning and melting, vitamin a, vitamin c, vitamin ...
• Plant cells may swell (become turgid), but they cannot burst or rupture (lyse) like animal cells • Equally, the cell membrane may shrink from the cell wall (plasmolysis), but overall structure remains intact Direct Active Transport (Primary): ATP hydrolysis is used to mediate transport by causing a conformational
Lipids and fatty acids create the membranes of the mitochondria. Nucleic acids create the DNA and RNA that are necessary for the mitochondria to even exist. (ATP is one of these nucleic acids)! Most of the enzymes used in Cell Respiration are proteins.
Bozeman tour of the cell worksheet answers ... eukaryotic cells which makes energy available to the cell in the form of ATP molecules phospholipids bilayer phoscole molecules Folipids which makes up a large saclike vacuole plasma membrane organelles which stores and transports materials within a small cell organelles vesicle which stores and ...
a stepwise sequence of reactions in cells, with specific enzymes catalyzing each step. viii. activation energy the minimum amount of energy that colliding reactants must have in order for a chemical reaction to occur. Part B: Short Answer: Complete the following on a separate sheet to be handed in for 17 marks .
Describe the role of proteins in the release of energy stored in ATP. ATP binds to a protein. The ATP is then broken down to ADP and Phosphate while it is attached to the protein. ADP and the phosphate are then released from the protein. The protein is a holder for the ATP to be broken down.




















0 Response to "35 the role of atp in cells worksheet answers"
Post a Comment