30 Motion In One Dimension Acceleration Worksheet Answers
to answer the following questions. a. A horizontal line means constant velocity (a = 0 m/s/s). b. A straight diagonal line means accelerating object. c. A gradually sloped line means small acceleration. d. A steeply sloped line means large acceleration. 4. The motion of several objects is depicted by a velocity vs. time graph. Answer the. UNIT 1: MOTION Worksheet D: I-Dimensional Motion Problems 've shown the answers that did not already appear on the handout. Note that it is important to insist that students show their givens, equation, substituted numbers with units, and a boxed answer with proper significant figures. Build good habits early on for showing all work.
Hint 1. Find out whether difference between the initial and final velociyt is positive or negative. Us the formula V-U+at to determine whether the acceleration is positive or negative. Click here to See Answer. Answer 1. Initial velocity u = 1 m/s. Final velocity v = 4 m/s. Velocity is becoming more positive as. v - u = 4 - 1 = 3 m/s is positive.
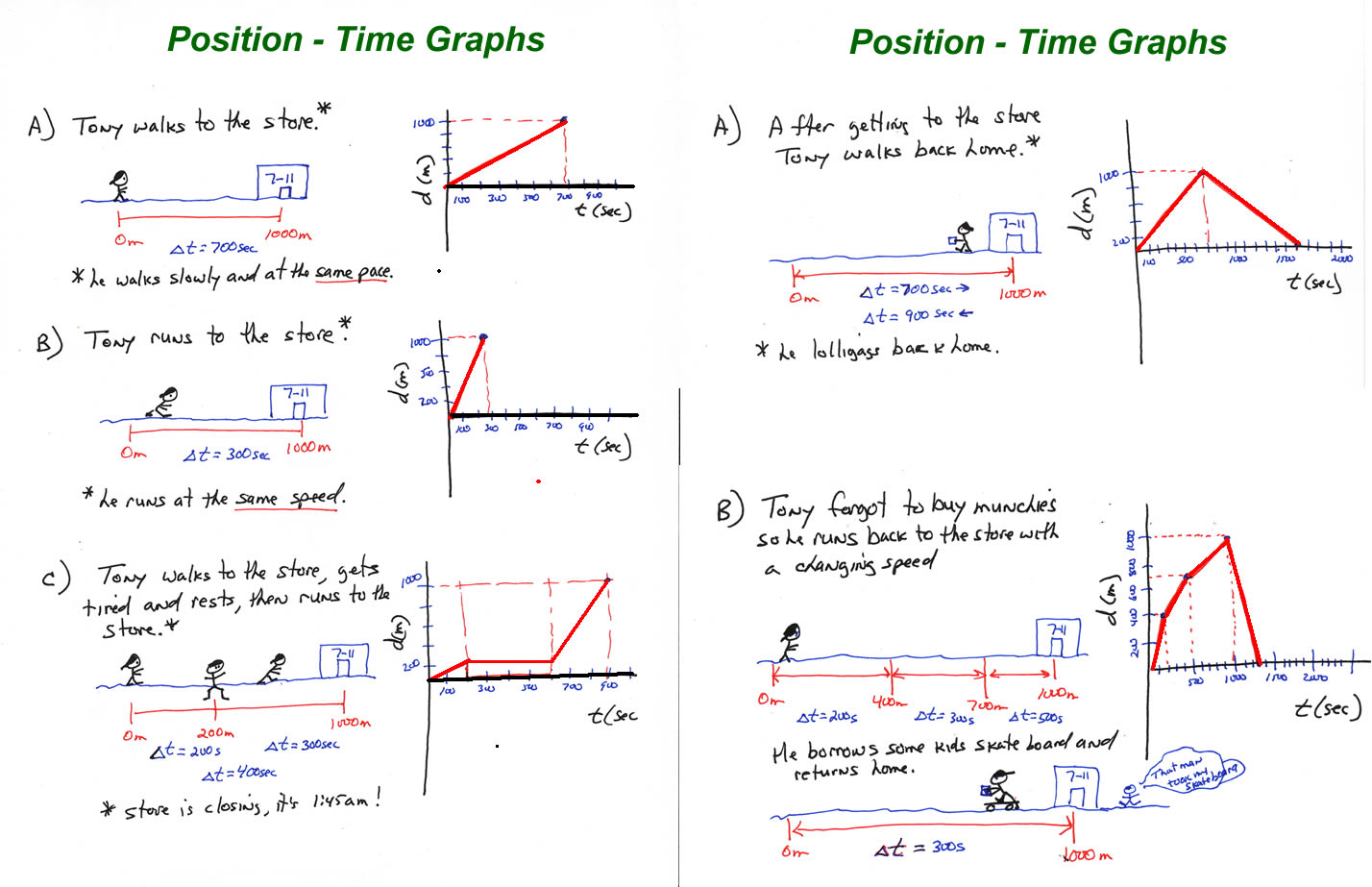
Motion in one dimension acceleration worksheet answers
Motion in one dimension worksheet answers pdf. The goal of kinematics is to mathematically describe the trajectory of an object over time. In this page we have sample problem and solutions in one dimensional motion. At an altitude of 1 00 km the rocket engine cuts off. Translate the above equations of linear motion to one dimensional vertical. Motion in Two Dimensions Problems and Solutions. admin May 31, 2019. Some of the worksheets below are Motion in Two Dimensions Problems and Solutions, Two-dimensional motion : Why We Study Motion in Two Dimensions, Vector Equations Reduce to Component Equations, Problem-Solving Techniques, Sample Problem,.. Once you find your document (s. One Dimensional Motion Worksheet Solve the following problems on a separate sheet of paper. Show all work using the prescribed problem solving method. 1. A car moving at 10 m/s speeds up uniformly to a speed of 30 m/s in a time of 5 seconds. What was the car’s acceleration? 2Answer: 4 m/s 2.
Motion in one dimension acceleration worksheet answers. A rock is released from rest from the top of a very high cliff, and accelerates downward at g. Comments and help with motion in one dimension problem a worksheet answers. Phys101 motion in one dimension spring 2014 3.the position function x(t) of a particle moving along an x axis is x = 4.0 6.0t2, with x in meters and t in seconds. One dimensional motion worksheet solve the following problems on a separate sheet of paper. Acceleration worksheet with answers. Show all work using the prescribed problem solving method. Motion graphs worksheet with answer. In these formulas the acceleration is assumed to be constant. Teachers may print the entire packet or individual think. Holt physics motion one dimension answers sooner is that this is the record in soft file form. Suppose it took 2 0 min at a constant. Yes from t4 to t5 3. Yes from t1 to t4 and from t6 to t7. One dimensional motion worksheet solve the following problems on a separate sheet of paper. Motion in one dimension worksheet answers pdf. The goal of kinematics is to mathematically describe the trajectory of an object over time. In this page we have sample problem and solutions in one dimensional motion. At an altitude of 1 00 km the rocket engine cuts off. Translate the above equations of linear motion to one dimensional vertical.
Motion can be described using words, diagrams, numerical information, equations, and graphs. Describing motion with numbers can involve a variety of skills. On this page, we will focus on the use tabular data to describe the motion of objects. 1. Position-time information for a giant sea turtle, a cheetah, and the continent of North America are Motion in One-Dimension ©2011, Richard White www.crashwhite e. Use the graph to determine the ball's instantaneous velocity at time t = 10 ms. Explain briefly how you arrived at your answer. 8. A rocket, initially at rest, is fired vertically upward with an acceleration of 12.0 m/s2. At an altitude of 1.00 km, the rocket engine cuts off. Important questions on kinematics kinematics worksheet motion in one dimension practice paper acceleration worksheet with answers. Velocity is the rate of change of displacement with respect to time. See answer see solution below. The diagram below depicts the path of a person walking to and fro from position a to b to c to d. Physics 110 spring 2006 1 d motion problems and their solutions 1. Physics 01 01 intro and units pdf. So in order to help you with that we at worksheetsbuddy have come. Express your answer in g s where 1 g 9 8 m s2.
Kinematic equations relate the variables of motion to one another. Each equation contains four variables. The variables include acceleration (a), time (t), displacement (d), final velocity (vf), and initial velocity (vi). If values of three variables are known, then the others can be calculated using the equations. This page demonstrates the process with 20 sample problems and accompanying. Motion in one dimension. Motion in a straight line ncert solutions. Once the study of motion is explored in more detail the teacher will then. Important questions on kinematics kinematics worksheet motion in one dimension practice paper acceleration worksheet with answers. A determine the distance traveled by the object between t 0 s and t 8 s. Question 12. SURVEY. 30 seconds. Q. The equations of linear motion apply only if. answer choices. system velocity is constant. system acceleration is constant. the total motion of a system is in one dimension within its reference frame. Holt physics motion in one dimension worksheet answers. A car moving at 10 m s speeds up uniformly to a speed of 30 m s in a time of 5 seconds. Holt physics 1 section quizzes assessment motion in one dimension teacher notes and answers 2 motion in one dimension acceleration 1. Cd de ef and fg. Answer the following questions in terms of t and g.
Chapter 2 worksheet review of motion in one dimension. Motion in one dimension worksheet. Motion in one dimension instantaneous velocity acceleration kinematics equation 1 mixed kinematics problems free fall acceleration due to gravity graphing. Teachers may print the entire packet or individual think sheets and use them freely with their classes.
These MCQs on motion set have more than 60 questions on motion physics and you will find those in the embedded pdf with a total of 12 pages. You can scroll through the pages using the up and down arrow at the header of the embedded pdf. Motion-in-one-dimension-MCQ-V5. Related Posts: Force and Laws of motion numerical problems
Motion in One Dimension The following PDF files represent a collection of classroom-ready Think Sheets pertaining to the topic of Motion in One Dimension. The Think Sheets are synchronized to readings from The Physics Classroom Tutorial and to missions of the Minds On Physics program. Teachers may print the entire packet or individual Think.
Motion in One Dimension 2.1 The Important Stuff 2.1.1 Position, Time and Displacement We begin our study of motion by considering objects which are very small in comparison to the size of their movement through space. When we can deal with an object in this way we refer to it as a particle.
Understanding Motion in One Dimension Worksheet Answers. So as to have motion, then you have to move. 1-D motion is movement that's in only a single direction. A quantity that does not depend on direction is referred to as a scalar quantity. Anything under 12 point could possibly be too tiny.
Section two problem workbook solutions ii ch. The correct answer is c. The physics classroom 2009 answer key motion in one dimension. Motion in one dimension problem a worksheet answers. Which object s is are not moving. View test prep worksheets ak pdf from science 101 at serra catholic high school.
The velocity of a body at a given instant is called. A. instantaneous velocity. B. uniform velocity. C. non-uniform velocity. D. none of the above. View Answer. A. instantaneous velocity. This is all about MCQs on Motion in One Dimension. You may also like to read MCQs on Heat Transfer.
Motion in Two Dimensions Problems and Solutions. admin May 31, 2019. Some of the worksheets below are Motion in Two Dimensions Problems and Solutions, Two-dimensional motion : Why We Study Motion in Two Dimensions, Vector Equations Reduce to Component Equations, Problem-Solving Techniques, Sample Problem,.. Once you find your document (s.
Chapter 4 - Motion in Two Dimensions Page 3 Answer to Essential Question 4.4 Assuming that we can neglect air resistance, the relative mass of the balls is completely irrelevant. If B's mass was double A's mass, for instance, the force of gravity on B would be twice that on A, but both balls would still have an acceleration of g r, and the two balls would still hit the ground simultaneously.
To describe the motion of an object, we must be able to specify the location of the object at all times, and Figure 2.1 shows how to do this for one-dimensional motion. In this drawing, the initial position of a car is indicated by the vector labeled x 0. The length of x 0 is the distance of the car from an arbitrarily chosen origin. At a later.
A Guide to Motion in One Dimension Teaching Approach In this series we continue on from the series on vectors and scalars by investigating the differences between distance and displacement, as well as between speed and velocity. We investigate constant acceleration and distinguish between deceleration and negative acceleration.
equations. However, I will include two more for the sake of convenience. Remember that the acceleration is assumed to be constant! Deriving the Kinematics Equations: We use 4 quantities to describe kinematics: 1. Position (x or y) 2. Velocity (m/s) 3. Acceleration (m/s2) 4. Time (s) Note: Constant acceleration ⇒ 𝑎̅=𝑎 at all times.
One Dimensional Motion Worksheet Solve the following problems on a separate sheet of paper. Show all work using the prescribed problem solving method. 1. A car moving at 10 m/s speeds up uniformly to a speed of 30 m/s in a time of 5 seconds. What was the car’s acceleration? 2Answer: 4 m/s 2.
Ex: The skier's acceleration is positive. The acceleration is 4 m/s2. Speed-Time Graphs Constant acceleration is represented on a speed-time graph by a straight line. The slope of the line is the acceleration. The graph is an example of a linear graph, in which the displayed data form straight-line parts. Graphing Acceleration
Motion in One Dimension Study Notes, Worksheets, PPT's, and Summary Revision Notes for IB Physics HL/SL Topic 2.1 + Two-Dimensional Motion + AP Physics
motion class 9 numerical questions with answers (with PDF Download) Formula used. Question 1. A train accelerates from 36 km/h to 54 km/h in 10 sec. (i) Acceleration. (ii) The distance travelled by car. Answer.
Motion in one dimension instantaneous speed vs average speed worksheet answers. Solved: class worksheet: kinematics in one dimension kinem. Physics handouts electrostaticskey worksheet motion one dimension standing coloring pages newton's laws of pdf work and energy free body diagrams answers circular pe. Uniform circular motion angular displacement velocity acceleration worksheet answers.
Chapter 2 Worksheet - Review of Motion in One Dimension. The following graph shows the velocity of a moving object as monitored over a time period of 8 s. Use the graph to answer the questions that follow: (a) Determine the distance traveled by the object between t = 0 s and t = 8 s.
Motion in One Dimension 1. What do you understand by the terms (i) rest (ii) motion ? Support your answer by giving two examples each. Ans. (i) When a body does not change its position with respect to the surrounding, the body is said to be at rest. Examples : A lamp post, a table in a room. (ii) When a body changes its position with respect to the

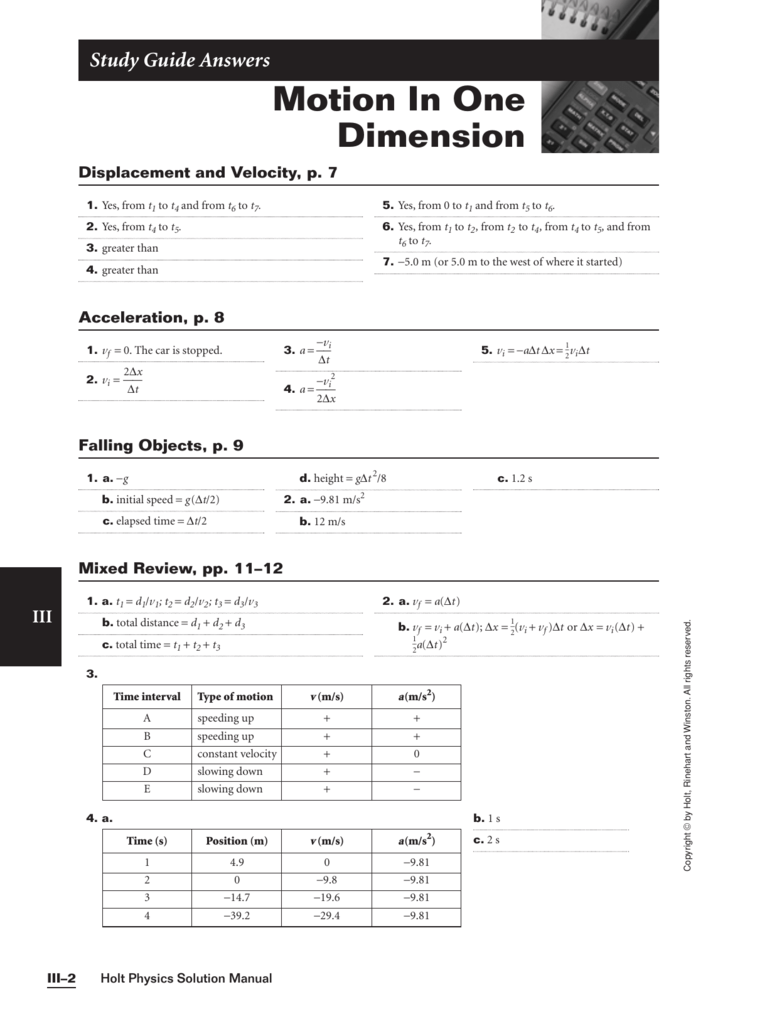




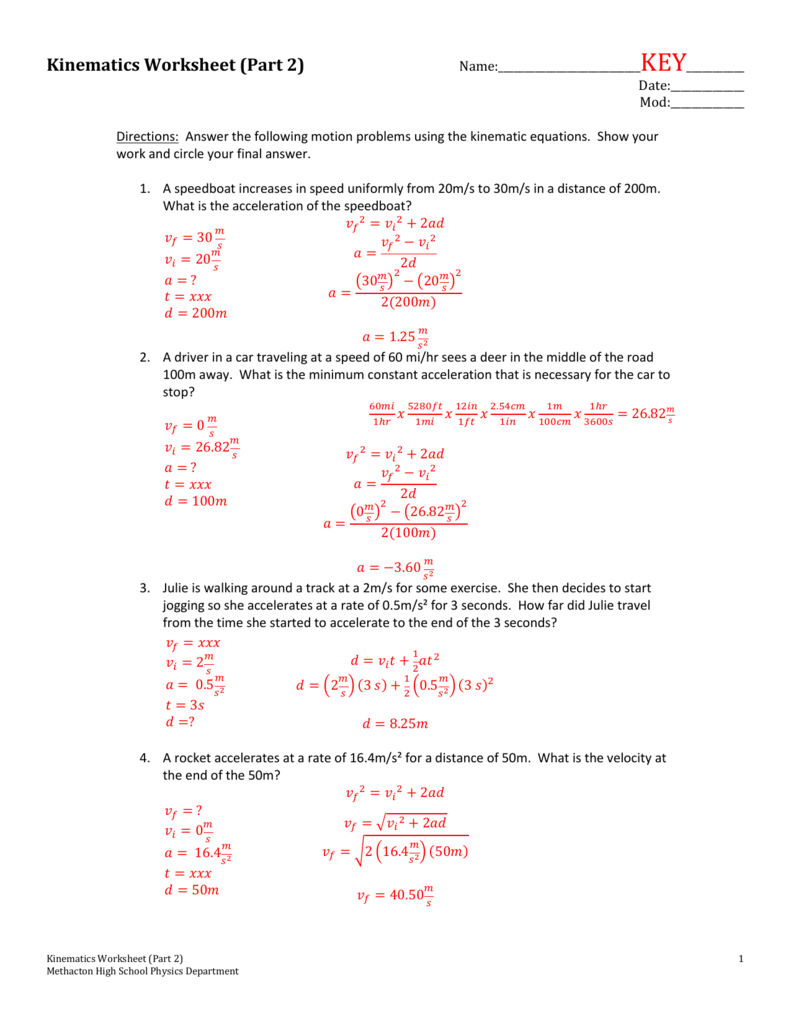







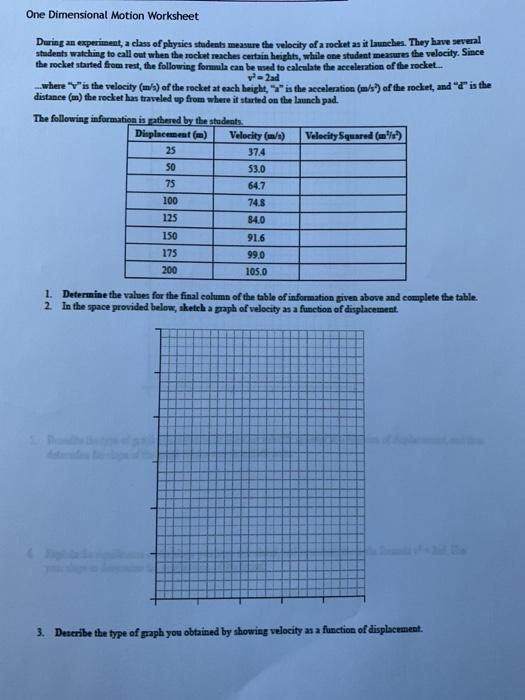
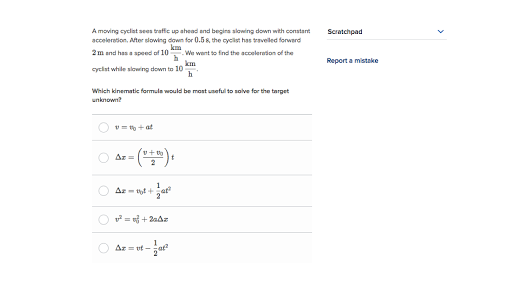




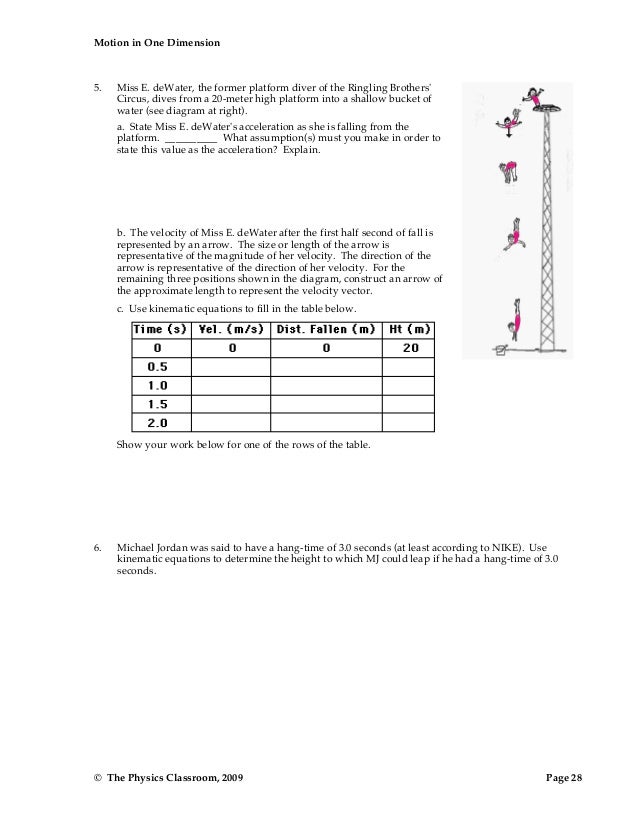
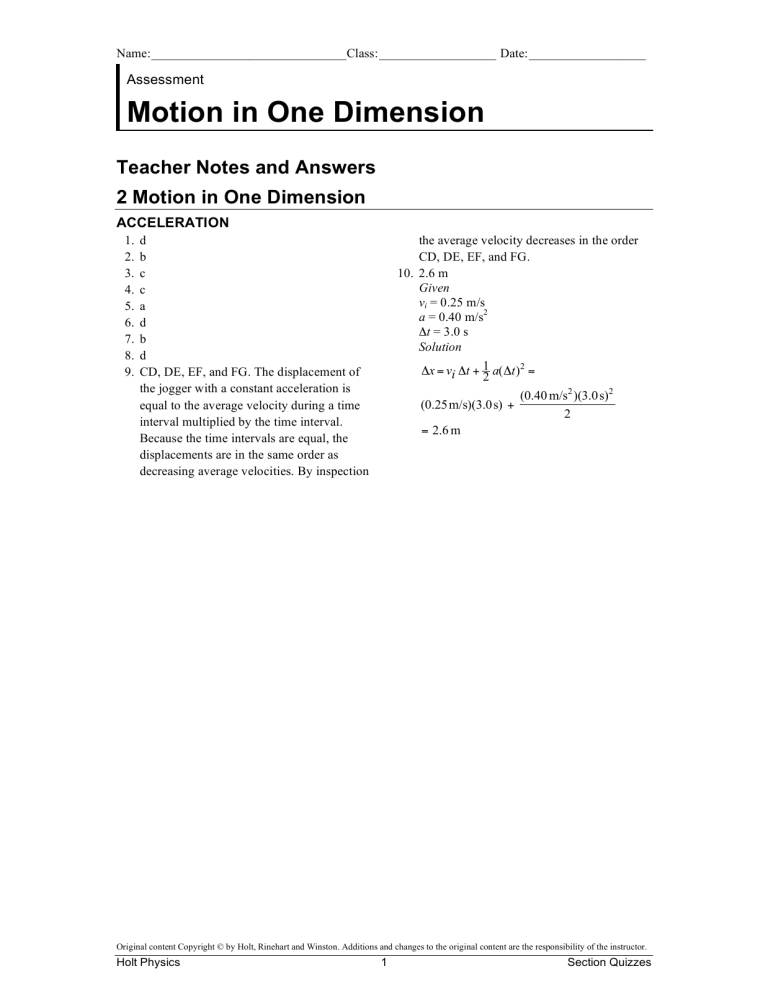


0 Response to "30 Motion In One Dimension Acceleration Worksheet Answers"
Post a Comment