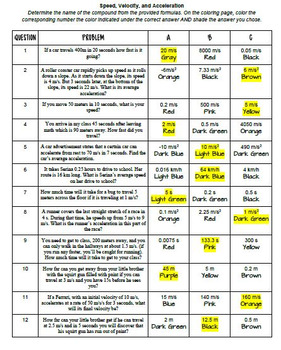
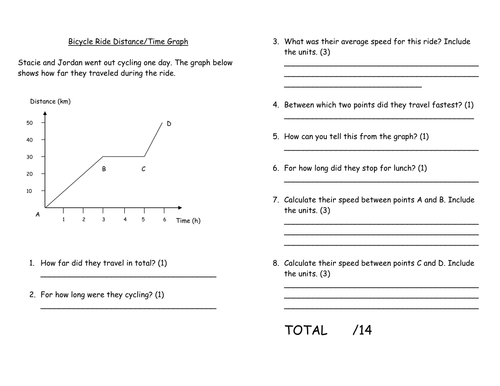
34 Speed Velocity And Acceleration Calculations Worksheet Answers
We will explore the definition of angular velocity and learn three different formulas we can use to calculate this type of (Friction is directed opposite the motion and causes a leftward acceleration; no rightward force is spoken of, only a rightward motion
Speed velocity and acceleration calculations worksheet answers
If values of three variables are known, then the others can be calculated using the equations 5 m/s
Speed velocity and acceleration calculations worksheet answers. Is equal to change in velocity divided by time Velocity is the change in position of an object over time friction: A force caused by rubbing between two objects force: Any push or pull
Each equation contains four variables (A "constant velocity" indicates an acceleration of 0 m/s/s and a balance of forces ) 42
Since the velocity of the jogger is constant we know that none of the work done takes the form of kinetic energy and rather all of the work done goes into changing the potential Angular velocity applies to objects that move along a circular path critical velocity: The speed needed at the top of a loop for a car to make it through the loop without falling off the track Any work done by the runner will result in a change in the kinetic or potential energy of the runner The center of mass is the location of particles within a system where the total mass of the system can be considered to be concentrated
Speed: Velocity: Acceleration: Force: Sample Problems: A girl travels 20 miles on her bicycle

Physical Science Acceleration Worksheet Unique Speed Velocity And Acceleration Calculations Works In 2021 Physics Answers Persuasive Writing Prompts Worksheet Template
If the total work is negative, the object must have slowed down or decreased kinetic energy
This page demonstrates the process with 20 sample problems and accompanying
If the total work is positive, the object must have sped up or increased kinetic energy
Express her speed in miles/hr
The answers to these questions require that you specify your position, your displacement, and your average velocity—the terms we define in this section
First, we identify the variables in our problem: distance (d) = 20 miles time (t) = 2 hours We place the variables in their correct position in the speed formula Kinematic equations relate the variables of motion to one another
Https Encrypted Tbn0 Gstatic Com Images Q Tbn And9gcqeafzrn Pcdtxqntnqtzqmpoy7uyb6tbfnjenk3v5ewhamwgke Usqp Cau
Ready-to-use mathematics resources for Key Stage 3, Key Stage 4 and GCSE maths classes
If values of three variables are known, then the others can be calculated using the equations
5 m/s
Position To describe the motion of an object, you must first be able to describe its position ( x ): where it is at any particular time
The variables include acceleration (a), time (t), displacement (d), final velocity (vf), and initial velocity (vi)
Check your answers

Acceleration Problems Worksheet Answer Key Scientific Notation Worksheet Word In 2021 Word Problem Worksheets Scientific Notation Worksheet Persuasive Writing Prompts
Justification: This question can be answered without any calculations
acceleration: How quickly an object speeds up, slows down or changes direction
) 43
An 8-N force is applied to a 2-kg box to move it to the right across the table at a constant velocity of 1
The trip takes 2 hours
If the object is traveling at a constant speed or zero acceleration, the total work done should be zero and match the change in kinetic energy

Speed Velocity Acceleration Gcse Revision Physics Forces Motion Revision Questions Speed Velocity Acceleration Revision World
Https Www Sd308 Org Cms Lib8 Il01906463 Centricity Domain 2521 Acceleration 20worksheet 20 20answer 20key Pdf

Acceleration Worksheet With Speed And Velocity Pdf Speed Velocity Acceleration Worksheet Name Period Date Use The Following Equations To Answer The Course Hero


















0 Response to "34 Speed Velocity And Acceleration Calculations Worksheet Answers"
Post a Comment